PyTorch Image Classification: A Step-by-Step Guide (+ An Alternative Method)

For this article, we hired Becca Miller, a freelance software developer and technical writer, to walk through the PyTorch and Nyckel image classification processes. Becca details her experience with both ML services and shares how you can build the image classifier yourself with either option.
Image classification is a common application of machine learning that trains computers to recognize and categorize images into labels. In this article, I’ll demonstrate how you can build an image classification model with PyTorch, a prominent deep learning framework.
Then, I’ll compare how you can solve image classification tasks with Nyckel, a specialized AutoML platform that does most of the ML heavy-lifting for you.
To facilitate a detailed comparison of these two solutions, I will work with a publicly available dataset that contains a diverse array of cat and dog images. My goal is to train an image classifier using both PyTorch and Nyckel by leveraging the technique of transfer learning. Transfer learning allows you to use pretrained models that have been extensively trained on large datasets, which enables you to fine-tune and adapt these models for a specific classification task. The main benefit of transfer learning is that you can train a model without needing a significant amount of data.
Through this comparison, I will:
- demonstrate how to use PyTorch or Nyckel for image classification,
- provide an in-depth analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of each approach, and
- equip you with a comprehensive understanding of both methodologies, so you can make an informed decision based on your precise requirements and constraints.
Image classification dataset
Before training the image classification models, I’m first going to break out a smaller section of the dataset. The dataset is large, including 8,007 training images and 2,025 testing images. However, since I’m applying transfer learning, I don’t really need all that data. I’ll use 100 cat photos and 100 dog photos for training and 20 photos of each for validation. This subset provides a manageable dataset that serves as an ideal starting point to illustrate the image classification process with PyTorch and Nyckel.
How to create a PyTorch image classification function
I’ll start by building an image classifier with PyTorch and walk you through the essential steps involved in training a function with PyTorch. You can also access a Jupyter notebook demonstrating this process.
1. Prepare your data
Before diving into model training, I first need to ensure that the data is properly prepared. To prepare the data, I’ll load and preprocess the images to create a suitable input format for the neural network. Using PyTorch’s data preprocessing tools, I can organize and format the data for model training.
2. Import a model for pretrained embeddings
PyTorch is compatible with various pretrained models. For this example, I will use OpenAI’s CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining) model for the foundational model. CLIP combines vision and language learning and provides excellent performance for classification tasks with small amounts of data.
3. Train your image classifier
Fine-tuning the CLIP model in PyTorch is challenging, despite the availability of preprocessed data and feature embeddings. The task involves choosing appropriate fine-tuning methods and adjusting hyperparameters to achieve optimal performance. While PyTorch offers a diverse library of useful functions, fine-tuning the CLIP model still demands an in-depth understanding of advanced machine learning techniques. I’ll need to manually configure the fine-tuning process with appropriate hyperparameters, which can often require continual experimentation and refinement to achieve the desired results.
4. Evaluate PyTorch’s image classification model
Once I’ve trained the image classifier, I can move on to evaluating its performance. This step is crucial to assess the model’s ability to correctly identify and categorize images. When testing the model, I see that it achieves an accuracy of 97% on the testing dataset.
I can also evaluate the model’s performance via a confusion matrix, which offers insights into the classifier’s ability to correctly classify and differentiate between different classes:
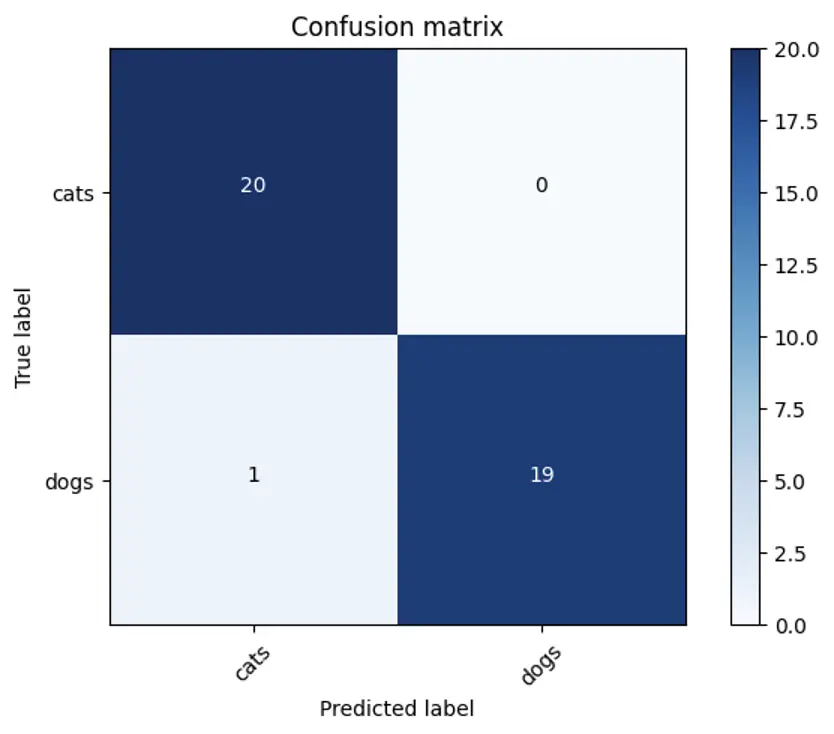
5. Package the image classification model as a Docker container
Once I’m happy with the model’s performance, I can package it as a Docker container so that I can deploy it to the target environment.
Image classification with Nyckel Python SDK
Now, I’ll dive into the image classification process using the Nyckel. I’ll demonstrate how to train an image classification function with labeled samples and how to invoke the trained model.
With Nyckel, you can choose to use the Nyckel Python SDK or do everything from Nyckel’s interface. For this example, I’ll use the Python SDK.
Since Nyckel automates much of the machine learning process, this really only involves two steps. Later in the article, I detail just what Nyckel does in the background to make the process so simple for the end user.
1. Use Python code to train your model
Here is all the code you need to train your model:
import os
from nyckel import User, ImageClassificationFunction
user = User(client_id="", client_secret="")
# Set the paths for the training and testing datasets
train_data_dir = 'cats-or-dogs/train'
test_data_dir = 'cats-or-dogs/test'
cats_dir = '/cats'
dogs_dir = '/dogs'
train_cat_dir = train_data_dir + cats_dir
train_dog_dir = train_data_dir + dogs_dir
test_cat_dir = test_data_dir + cats_dir
test_dog_dir = test_data_dir + dogs_dir
train_cat_files = os.listdir(train_cat_dir)
train_dog_files = os.listdir(train_dog_dir)
test_cat_files = os.listdir(test_cat_dir)
test_dog_files = os.listdir(test_dog_dir)
training_data = \[]
# Get all the filenames in the folder
for file in train_cat_files:
filename = train_cat_dir + '/' + file
training_data.append((filename, 'cats'))
for file in train_dog_files:
filename = train_dog_dir + '/' + file
training_data.append((filename, 'dogs'))
func = ImageClassificationFunction.new("IsCatOrDog", user)
func.create_samples(training_data)
2. Evaluate Nyckel’s image classification model
Because Nyckel automatically chooses the best model, cross-validates your data, and handles deployment (more on that in the next section), I’m already ready to evaluate the model. Nyckel uses metrics such as precision, recall, and F1 to automatically assess the performance of a trained model.
When evaluating the model, I see that it achieves an accuracy of 100% on the training data, correctly identifying all images as cats or dogs. I can also quickly evaluate the model’s performance on the testing set.
To see how the model performs on individual labels, I can use the following code:
for file in test_cat_files:
filename = test_cat_dir + '/' + file
prediction = func(filename)
print('predicted label: {}, true label: cats'.format(prediction.label_name))
for file in test_dog_files:
filename = test_dog_dir + '/' + file
prediction = func(filename)
print('predicted label: {}, true label: dogs'.format(prediction.label_name))
With this, I can see that the model correctly classifies all data in the testing set, too. All 20 dogs are correctly classified as dogs, and all 20 cats are correctly classified as cats. I can visualize this performance with a confusion matrix:
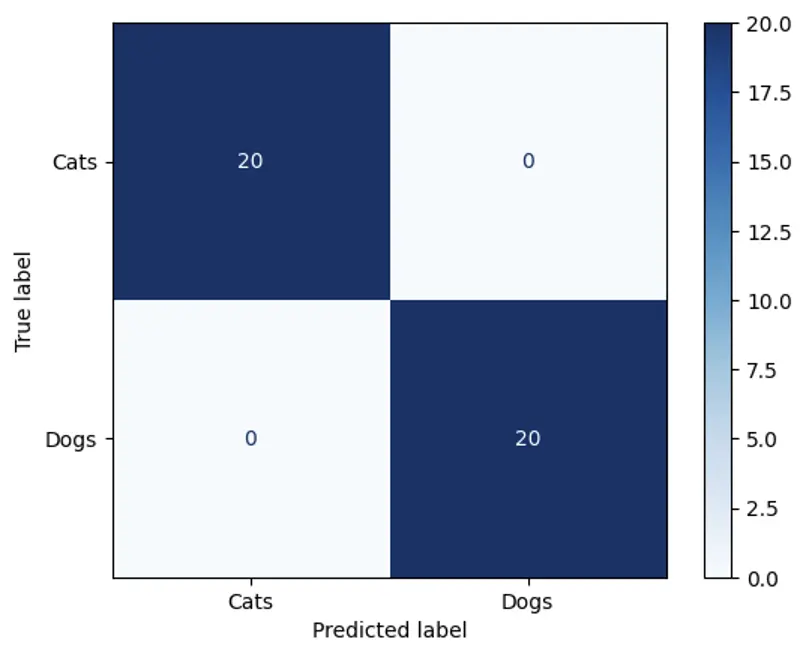
Understanding how Nyckel works
As an AutoML platform, Nyckel automates much of the machine learning development process for you, making the tool accessible to both machine learning novices and experts. Here are a few of the features the platform includes:
Exploration of various model types
Nyckel automatically explores multiple base models, fine-tuning methods, and hyperparameters to find the best model for your dataset. By automating this process, Nyckel encodes best practices for training while eliminating the tedium of evaluating various models and training methods manually.
Training via cross-validation
Nyckel uses cross-validation to train its models, a method that involves resampling the data so that different data segments are used for model testing and training on each iteration. This process is a data efficient way to train a model, allowing you to generate models with less training data. Additionally, the model’s performance on cross-validated data suggests how it will likely perform on independent test sets.
Simple deployment
When Nyckel trains your model, it is instantly deployed to hardware that scales up or down depending on your usage. It can be integrated into your application through an API call.
Image classification using Nyckel’s UI
Nyckel provides a user-friendly interface as an alternative to the Python SDK, simplifying the image classification process for users who prefer a web interface. With Nyckel’s UI, users can manage and monitor their image classification tasks without the need for coding, making Nyckel accessible to users without coding or machine learning experience. Additionally, the Nyckel UI can be used independently or in conjunction with the Python SDK.
You can see how the Nyckel UI works in this demo:
Nyckel’s dashboard provides users with access to a range of powerful tools, including a data engine that allows users to inspect and iterate on data used to train the model. Through this dashboard, users can examine the model’s performance on specific data inputs and improve the model in real-time. Users can identify the kinds of data where the model performs poorly and introduce new data inputs to address these limitations, ultimately improving model performance.
That platform also offers an invoke capture feature which automatically and intelligently captures informative data as you invoke your models and then places it in a queue for your team to review and annotate later. As you annotate this data in Nyckel’s dashboard, Nyckel retrains your model on this new data and redeploys the improved model.
PyTorch vs. Nyckel: Which is right for you?
When considering the choice between PyTorch and Nyckel for your image classification tasks, it’s essential to evaluate your specific requirements and expertise level. PyTorch is a good fit for experienced ML users who seek a wide range of customization and deployment options, while Nyckel provides a solution for users looking to simplify the image classification process.
PyTorch
- Fine-grained control: Provides advanced users with the ability to finely control the model and hyperparameters, allowing for meticulous customization and optimization.
- Hardware flexibility: Enables the deployment of trained models on a wide range of hardware, ensuring adaptability to various infrastructure setups.
Nyckel
- Model optimization: Conducts an extensive model and hyperparameter sweep, increasing the likelihood of finding an optimized model with embedded best practices for superior performance.
- Reliable results: Integrates cross-validation techniques to enhance model reliability and accuracy, ensuring robust performance even in complex, real-world scenarios.
- Efficient deployment: Automatically deploys models to elastic and cost-optimized hardware, facilitating seamless scalability and efficient resource utilization.
- Automated retraining: Automatically retrains the model as new data is added, eliminating the need for manual retraining and saving valuable time and resources.
- Data engine: Utilizes a robust data engine for streamlined data management, allowing for dynamic data analysis and refinement in tandem with the trained model.
- Invoke capture: Provides the capability to invoke capture, enabling the capture of real-time insights for continuous refinement and enhancement of the image classification model.
While PyTorch offers a high level of customization and flexibility for experienced machine learning practitioners, Nyckel offers a user-friendly platform that simplifies the image classification workflow without compromising performance and reliability. Nyckel’s intuitive interface and comprehensive features facilitate the image classification process, helping users achieve excellent results with improved efficiency. Its automated features and integration with advanced data management tools make it an ideal choice for users looking for an easy-to-use yet high-performing image classification solution.
Would you like to explore how Nyckel could solve your image classification task? Sign up for a free account or reach out to us at any time for support along the way.
